Method of Electron Resonance Imaging
What is the Electron Resonance Imaging?
ERI stands for Electron Resonance Imaging. This is a new method of functional imaging based on Electron Paramagnetic Resonance.
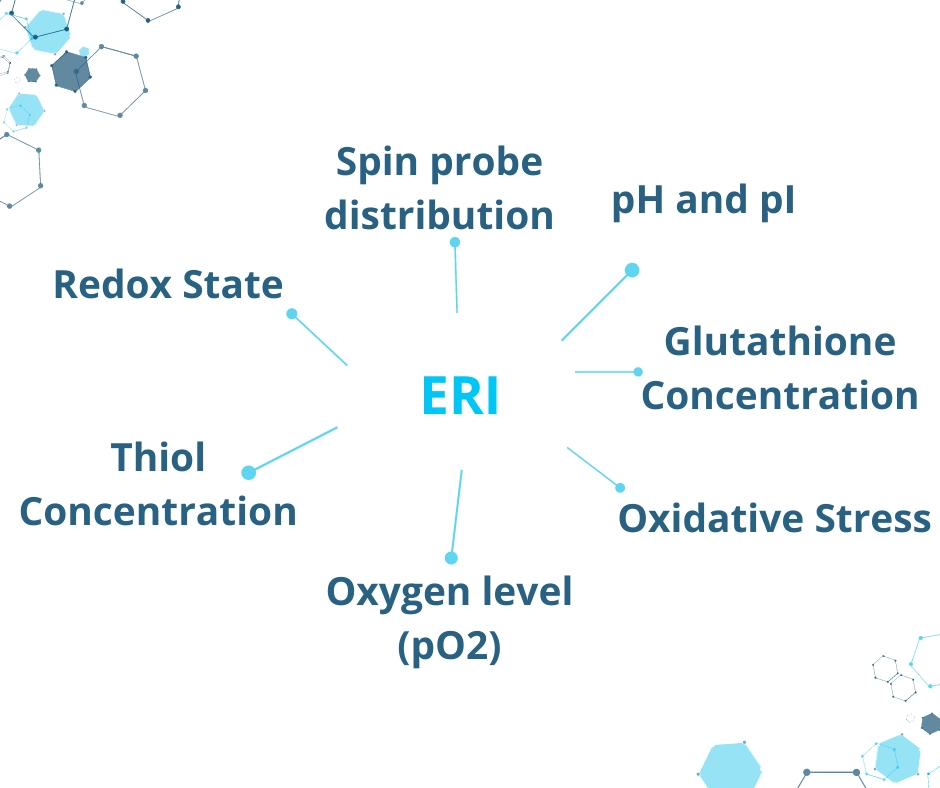
The ERI technique uses a combination of a suitable magnetic field and the injection of an external spin probe into an animal. Specifically, spin probes, which are used in the ERI technique, belong to the family of nitroxides or trityls. Furthermore, the physiological environment inside an animal’s body affects the spectral properties of the spin probe, which contains an unpaired electron. Consequently, it is possible to monitor unique biological parameters such as the absolute level of oxygen, redox state, pH changes, and oxidative stress.

Areas of application
- Monitoring of oncology therapies and imaging of their effects
- Diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases
- Detection for areas of hypoxia and oxygen concentration, as well as examination of their mechanisms
- ROS imaging and studies of oxidative stress
- Whole-body spin probe mapping in small rodents (diameter up to 34 mm)
- Imaging of redox state in different brain disorders
Experts Explain Theory of Electron Resonance Imaging 👉🏼
Our specialists will guide you in exploring new horizons in preclinical imaging. Experience the in vivo applications of ERI and discover the diverse fields where this cutting-edge technique can be applied.
Resolution parameters
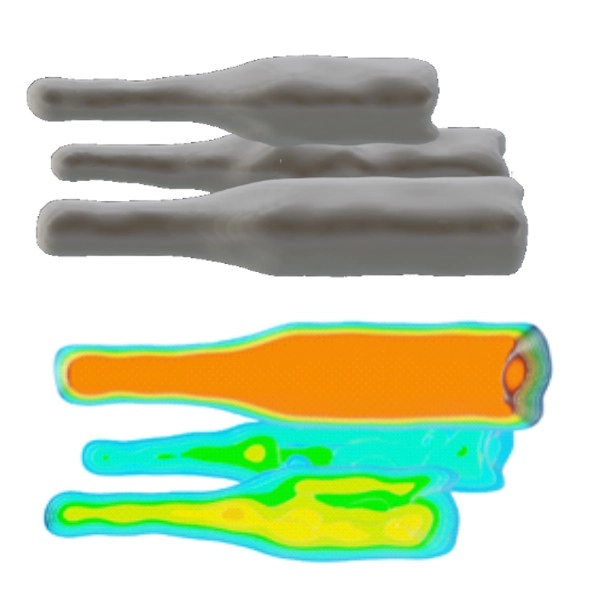
Three 10 mm long bottles with OXO71. 3D rendered images of the surface and distribution of the spin density
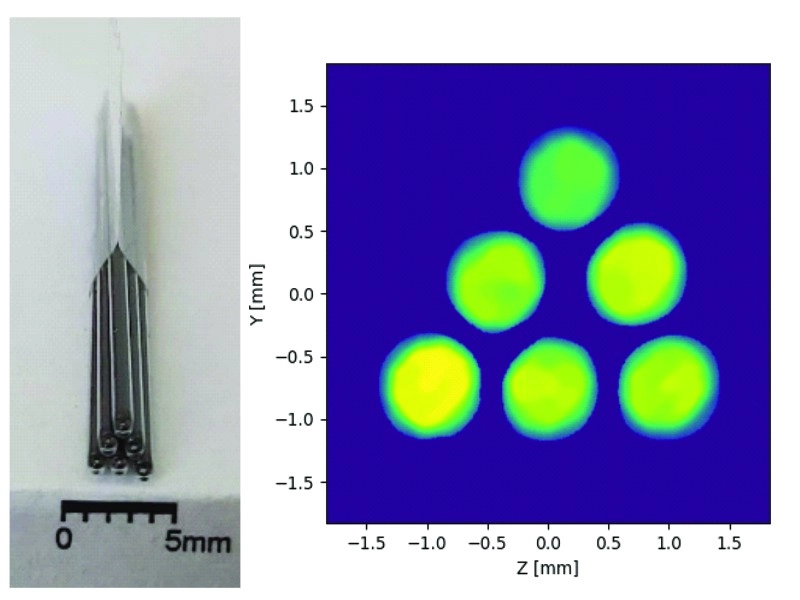
Picture and reconstruction of a bunch of capillaries filled with marker, inner diameter 0,7mm.
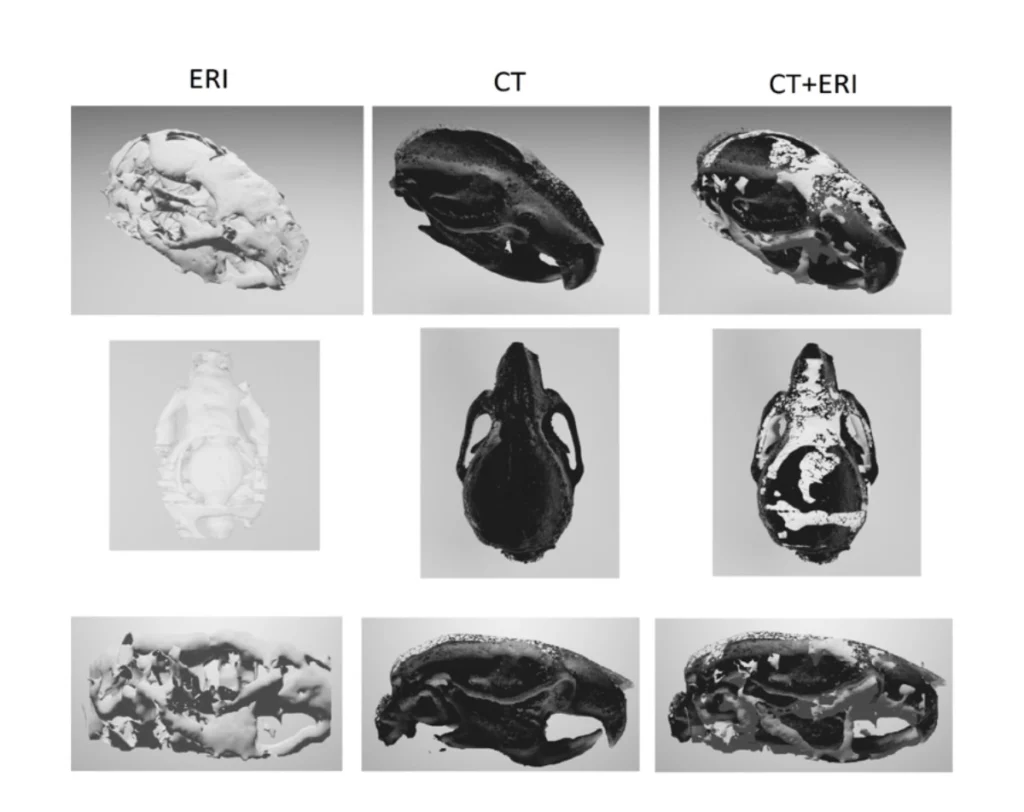
The results indicate the correct mapping of the skeletal system, with the thickness of which is about 100 µm.
The images obtained with ERI
doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c05703.
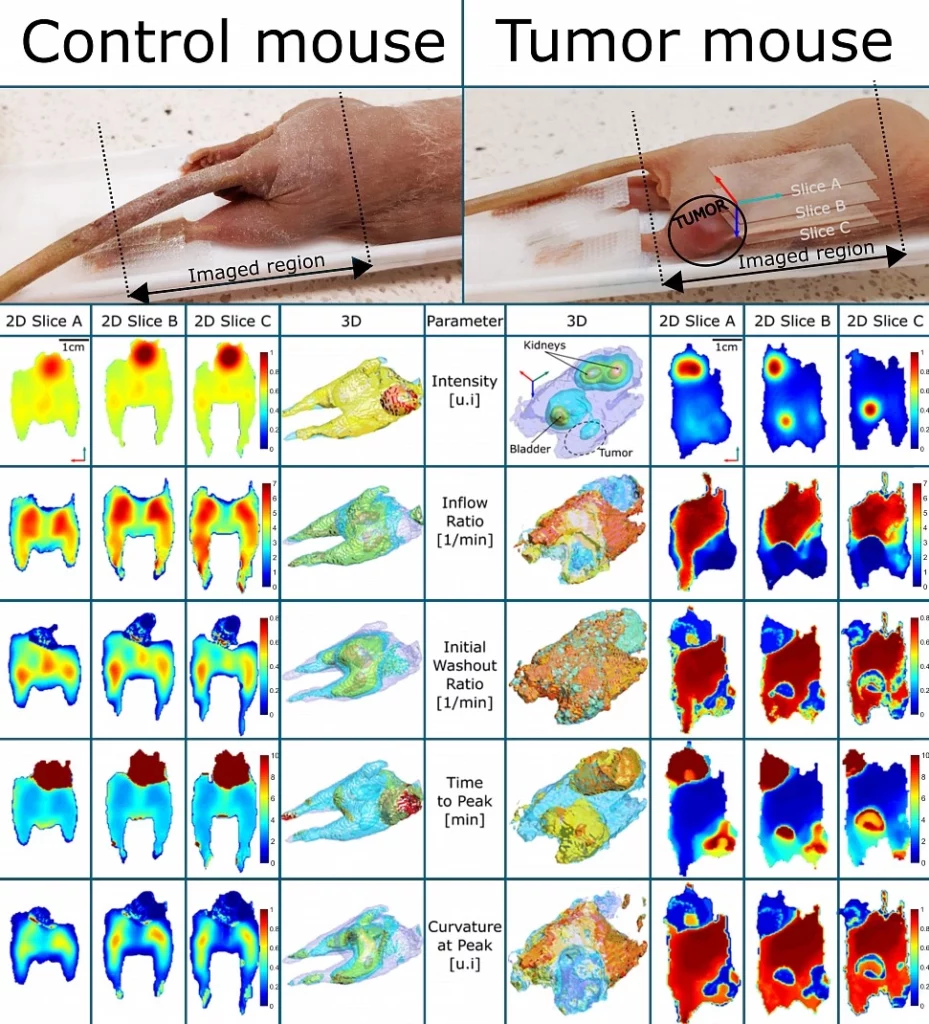
Imaging of control and tumour mouse in ERI TM600

Imaging of mouse brain in ERI TM600

